Suppose, while traversing the array you encounter a 132 pattern that violates the non-decreasing property. Now you have 2 options to fix this anomaly.
a=1, b=3, c=2
- Either we decrease
b and make it equal to c i.e.b=c=2. - Or we increase
c to make it equal to b i.e. c=b=3.
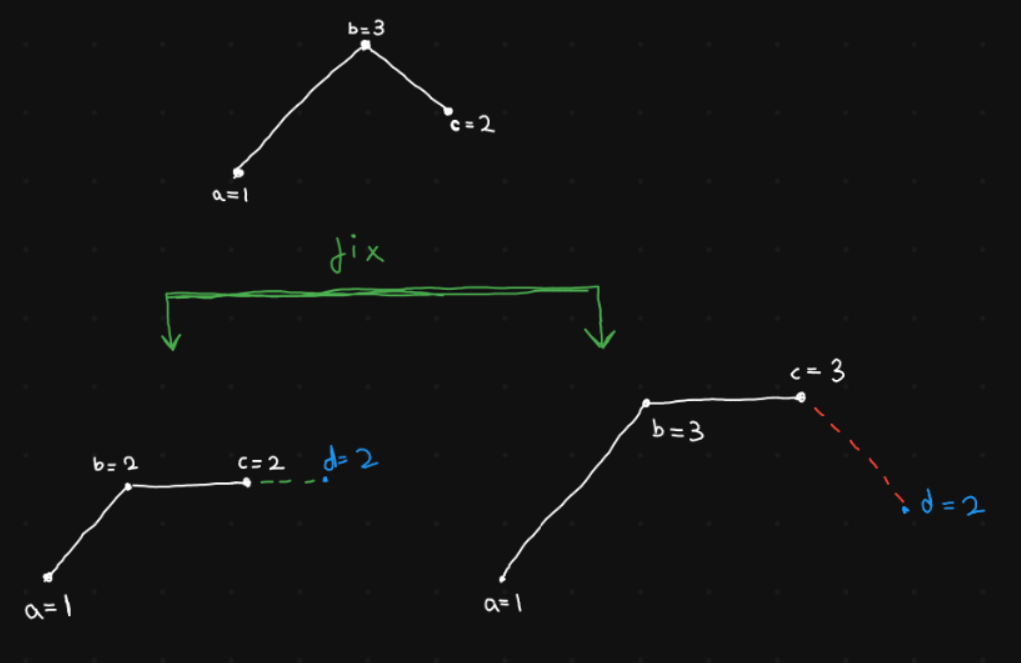
I would argue that we should always try to decrease b. Since, it enables us to have lower last value i.e. c. It decreases the chance of next number in the sequence violating the non-decreasing property.
In the same example, suppose, we had another number d=2. The the first case, we can accomodate d, to make the sequence 1222. While in the second case, we are unable to accomodate d, since that would make the sequence 1332 (invalid)
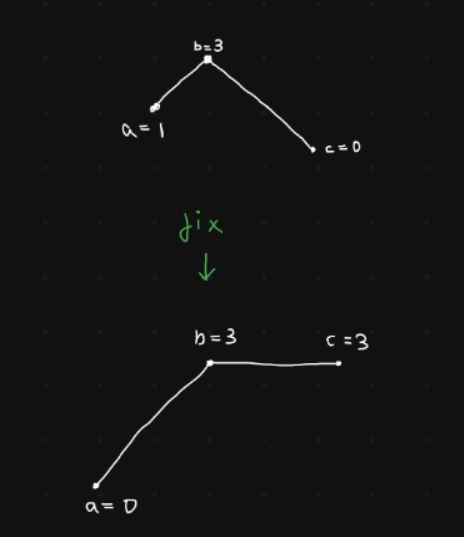
There is one exception to this rule.
Suppose we encounter a 130 pattern. In this case, our only option to fix the sequence is to make c=b=3, so that the pattern becomes 133.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| class Solution:
def checkPossibility(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
cnt_violations=0
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i-1] > nums[i]:
cnt_violations+=1
if cnt_violations > 1: return False
# only in 130 pattern shall you increase nums[i]
if i-2 >= 0 and nums[i-2] > nums[i]:
nums[i] = nums[i-1]
# 132 pattern -> decrease nums[i-1]
else:
nums[i-1] = nums[i]
return True
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution {
public:
bool checkPossibility(vector<int>& nums) {
int cnt_violations = 0;
for ( int i=1; i < nums.size(); i++ ) {
if ( nums[i-1] > nums[i] ) {
cnt_violations++;
if ( cnt_violations > 1 ) return false;
// only when 130 pattern, shall you increase nums[i]
if ( i-2 >= 0 && nums[i-2] > nums[i] ) {
nums[i] = nums[i-1];
}
// 132 pattern -> decrease nums[i-1]
else {
nums[i-1] = nums[i];
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| bool checkPossibility(int* nums, int numsSize)
{
int cnt_violations = 0;
for ( int i=1; i < numsSize; i++ ) {
if ( nums[i-1] > nums[i] ) {
cnt_violations++;
if ( cnt_violations > 1 ) return false;
// only when 130 pattern, shall you increase nums[i]
if ( i-2 >= 0 && nums[i-2] > nums[i] ) {
nums[i] = nums[i-1];
}
// 132 pattern -> decrease nums[i-1]
else {
nums[i-1] = nums[i];
}
}
}
return true;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| class Solution {
public boolean checkPossibility(int[] nums) {
int cnt_violations = 0;
for ( int i=1; i < nums.length; i++ ) {
if ( nums[i-1] > nums[i] ) {
cnt_violations++;
if ( cnt_violations > 1 ) return false;
// only when 130 pattern, shall you increase nums[i]
if ( i-2 >= 0 && nums[i-2] > nums[i] ) {
nums[i] = nums[i-1];
}
// 132 pattern -> decrease nums[i-1]
else {
nums[i-1] = nums[i];
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| function checkPossibility(nums: number[]): boolean {
let cnt_violations = 0;
for ( let i=1; i < nums.length; i++ ) {
if ( nums[i-1] > nums[i] ) {
cnt_violations++;
if ( cnt_violations > 1 ) return false;
// only when 130 pattern, shall you increase nums[i]
if ( i-2 >= 0 && nums[i-2] > nums[i] ) {
nums[i] = nums[i-1];
}
// 132 pattern -> decrease nums[i-1]
else {
nums[i-1] = nums[i];
}
}
}
return true;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| function checkPossibility(nums) {
let cnt_violations = 0;
for ( let i=1; i < nums.length; i++ ) {
if ( nums[i-1] > nums[i] ) {
cnt_violations++;
if ( cnt_violations > 1 ) return false;
// only when 130 pattern, shall you increase nums[i]
if ( i-2 >= 0 && nums[i-2] > nums[i] ) {
nums[i] = nums[i-1];
}
// 132 pattern -> decrease nums[i-1]
else {
nums[i-1] = nums[i];
}
}
}
return true;
}
|

