This problem is very similar to
lc543,
which is about finding the longest edge path in a tree. You can just
copy over that code, and add 2 lines in it.
Here we are doing the same thing as in lc543, however, when we encounter a non-matching child. We treat it as null.
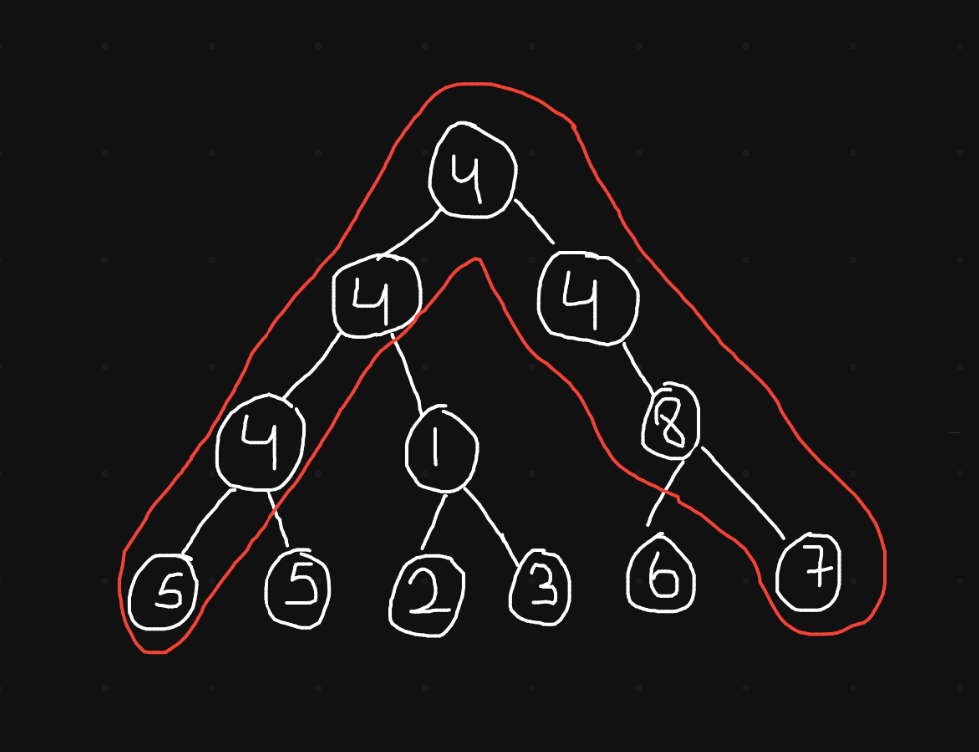
For example, here the longest path at root node is highlighted below in red with 6 edges.
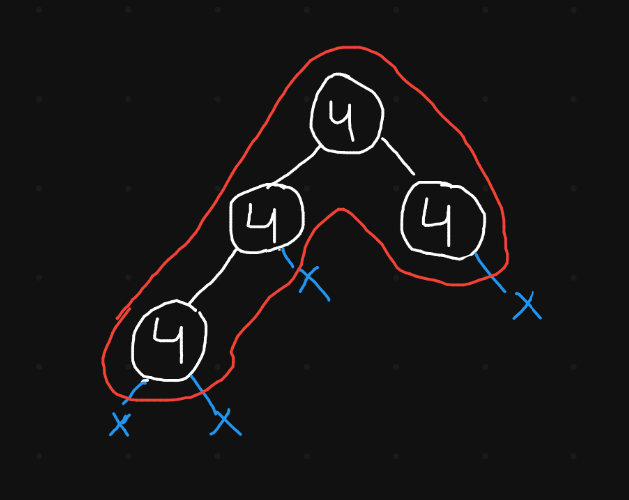
Our algorithm views the tree like this. The longest path of 3 edges is highlighted in red.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| int edges( struct TreeNode* node );
int longest_path;
int longestUnivaluePath(struct TreeNode* root)
{
longest_path = 0;
edges(root);
return longest_path;
}
int edges( struct TreeNode* node )
{
if ( !node ) return -1;
int left = edges(node->left),
right = edges(node->right);
// treat child as null if it doesn't match parent
left = (node->left && node->val == node->left->val)
? left : -1;
right = (node->right && node->val == node->right->val)
? right : -1;
longest_path = fmax(longest_path, 1+left + 1+right);
return 1 + fmax( left, right);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.ans = 0
def longestUnivaluePath(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.edges( root )
return self.ans
def edges(self, node: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not node:
return -1
left, right = self.edges( node.left ), self.edges( node.right )
# if the child is illegitimate. Discard it
if not node.left or node.left.val != node.val:
left = -1 # treat as null
if not node.right or node.right.val != node.val:
right = -1
self.ans = max( self.ans, ( 1+left ) + ( 1 + right ) )
return 1 + max( left, right )
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| function longestUnivaluePath(root: TreeNode | null): number {
let ans = 0;
const edges = ( node: TreeNode|null ): number => {
if ( !node ) return -1;
let left = edges( node.left ),
right = edges( node.right );
// if child value doesn't match -> treat as null
left = (node.left && node.val == node.left.val)
? left : -1;
right = (node.right && node.val == node.right.val)
? right : -1;
ans = Math.max( ans, (1 + left) + (1 + right) );
return 1 + Math.max( left, right );
}
edges( root );
return ans;
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| function longestUnivaluePath(root) {
let ans = 0;
const edges = ( node ) => {
if ( !node ) return -1;
let left = edges( node.left ),
right = edges( node.right );
// if child value doesn't match -> treat as null
left = (node.left && node.val == node.left.val)
? left : -1;
right = (node.right && node.val == node.right.val)
? right : -1;
ans = Math.max( ans, (1 + left) + (1 + right) );
return 1 + Math.max( left, right );
}
edges( root );
return ans;
};
|

